What Is an Articulated Robot? Everything you need to know
By the RobotsTrader.com Staff | February 27, 2025

Introduction
Articulated robots are a staple in modern manufacturing, offering precision, flexibility, and efficiency across industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics. These robotic arms, designed with multiple joints, mimic human movement to perform tasks such as welding, assembly, and material handling with exceptional accuracy. In this guide, we’ll break down what an articulated robot is, its key components, how it’s programmed, and its real-world applications. Whether you’re looking to implement automation in your facility or gain a deeper understanding of robotic technology, this article will provide valuable insights.
What Is an Articulated Robot?
Understanding Multi-Joint Robotics
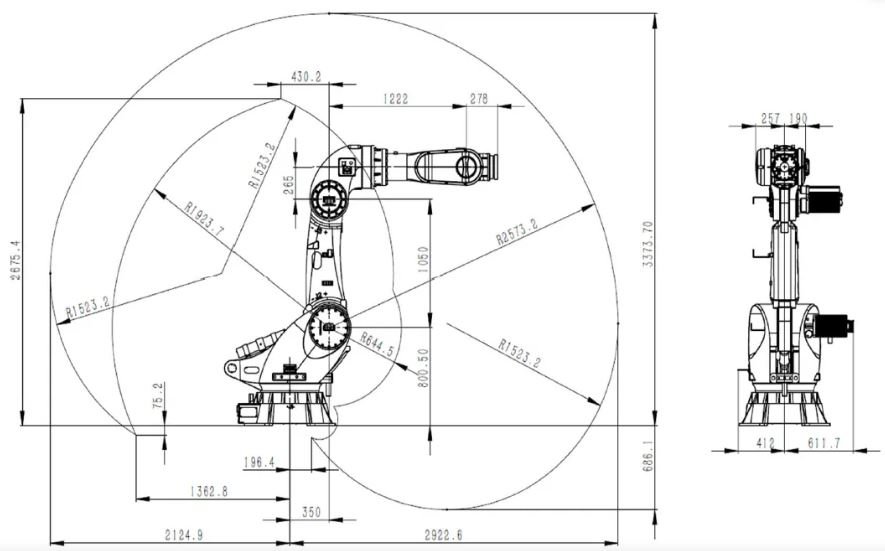
An articulated robot is an industrial robot with multiple rotary joints, allowing it to move in complex ways similar to a human arm. The number of rotary axes determines its degrees of freedom (DOF), with most industrial models featuring 4 to 7 axes:
- 4-Axis Robots – Ideal for palletizing and pick-and-place operations.
- 6-Axis Robots – The most common type, enabling full Cartesian (X, Y, Z) movement plus wrist rotation.
- 7-Axis Robots – Provide enhanced flexibility, useful in welding and intricate assembly tasks.
Why Choose an Articulated Robot?
Articulated robots offer several advantages over SCARA and Cartesian robots:
✔️ Greater flexibility – Can maneuver around obstacles and function in confined spaces.
✔️ Expanded range of motion – Essential for complex, multi-step operations.
✔️ Higher precision – Ideal for tasks requiring accuracy, such as welding and component assembly.
Key Components of Articulated Robots
1. Robot Controller – The Brain of the System
The robot controller is the central processing unit (CPU), executing commands and controlling movement. It processes operator inputs, sensor data, and motion algorithms to ensure smooth operation.

2. Teach Pendant – Programming Interface
The teach pendant is a handheld device used to program, test, and troubleshoot the robot. It allows operators to manually guide the robot and create task sequences.

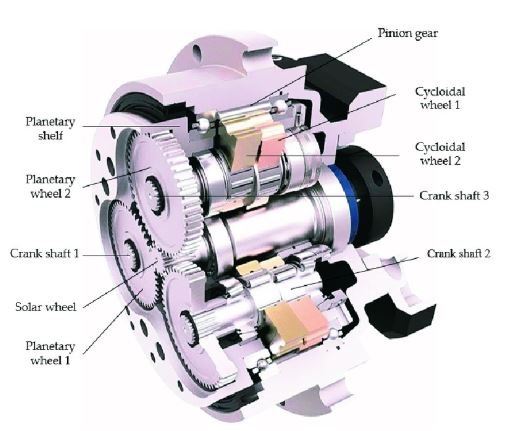
3. RV Reducers – Precision and Torque Control
An RV reducer (strain wave gear) enhances motion accuracy by providing high torque with minimal backlash, crucial for precise positioning and load handling.
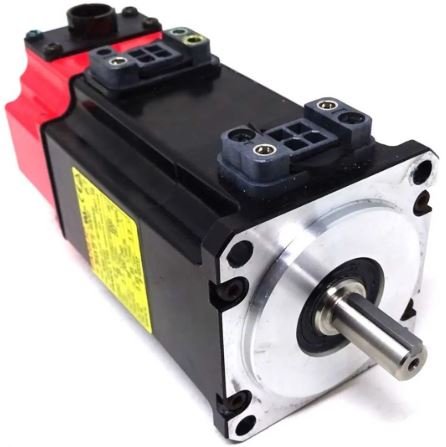
4. Servo Motors – Powering the Joints
Servo motors drive each joint, offering precise movement and torque control. These motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, ensuring smooth articulation.

Programming and Motion Control
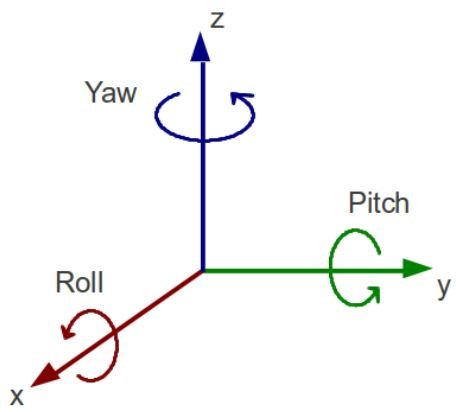
How Articulated Robots Move: Cartesian Coordinates
Articulated robots operate using Cartesian coordinates (X, Y, Z axes) combined with rotational movements (roll, pitch, yaw). Their controllers translate Cartesian inputs into joint-specific angles, enabling precise movement.
Programming Languages by Brand
Each manufacturer has its own proprietary programming language:
- Fanuc – KAREL & TP (Teach Pendant Language)
- ABB – RAPID
- KUKA – KRL (KUKA Robot Language)
- Yaskawa – INFORM
- Universal Robots – URScript (Python-based)
Example: Simple Pick-and-Place Program

Industry Applications of Articulated Robots
1. Automotive Manufacturing
Articulated robots are widely used in the automotive industry for welding, painting, and assembly. Models like the Fanuc R-2000iC and ABB IRB 6700 handle tasks such as spot welding car frames and installing components.
2. Electronics Assembly
Electronics manufacturers use articulated robots for precision placement, soldering, and circuit board assembly. Robots like the ABB IRB 1200 and Fanuc LR Mate series are ideal for high-speed micro-assembly operations.
3. Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace companies deploy articulated robots for drilling, riveting, and composite material handling. Models like the KUKA Titan Series and Fanuc M-900iB assist in assembling aircraft fuselages and inspecting critical components.
4. Warehousing & Logistics
Articulated robots enhance warehouse efficiency by automating palletizing, order fulfillment, and sorting. The Yaskawa MotoPick and Fanuc M-410 Series optimize high-speed packaging and shipment preparation.
The Future of Articulated Robots
- AI-Powered Robotics – Robots equipped with machine learning can adapt to new tasks without reprogramming.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots) – The rise of safe, human-friendly robots like the Fanuc CRX Series and Universal Robots UR10 is transforming production lines.
- Cloud-Based Automation – Remote-controlled robots with real-time diagnostics and monitoring capabilities.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Articulated Robot
Articulated robots are at the forefront of industrial automation, providing unmatched precision, speed, and versatility. Whether your operation requires high-speed assembly, complex welding, or heavy-load handling, the right robot can significantly enhance productivity. If you’re looking to buy or sell articulated robots, RobotsTrader.com is a trusted marketplace featuring new and used models from top manufacturers like Fanuc, ABB, KUKA, and Yaskawa. Explore listings and find the perfect automation solution for your business today.
Explore More Types of Industrial Robots
This article is part of our Used Industrial Robots 101: Basics of Automation Series, where we break down different types of industrial robots and their applications. If you’re interested in learning about other robotic systems, check out these in-depth guides:
🔹 Ultimate Guide to the Different Types of Industrial Robots – Explore the full range of industrial robots, including SCARA, Cartesian, and collaborative robots.
🔹 What Is a Delta Robot? A Complete Guide – Dive into delta robots, their high-speed design, components, and applications in automation.
🔹 What Is a SCARA Robot? – Discover SCARA robots, their high-speed precision, and cost-effective applications.

Leave a Reply